What is JAXB?
JAXB stands for Java architecture for XML binding.It is used to convert XML to java object and java object to XML.JAXB defines an API for reading and writing Java objects to and from XML documents.Unlike SAX and DOM,we don't need to be aware of XML parsing techniques.
There are two operations you can perform using JAXB
- Marshalling :Converting a java object to XML
- UnMarshalling :Converting a XML to java object
JAXB Tutorial
We will create a java program to marshal and unmarshal.
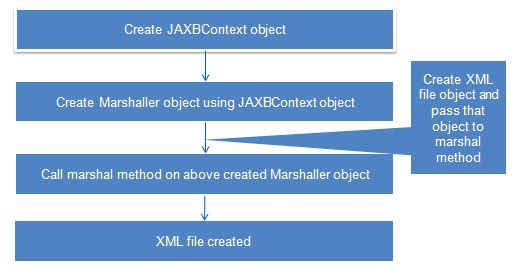
For Marshalling:
For Unmarshalling:
Java program:
With the help of annotations and API provided by JAXB,converting a java object to XML and vice versa become very easy.
1.Country.java
A Java object which will be used to convert to and from XMLCreate Country.java in src->org.arpit.javapostsforlearning.jaxb
package org.arpit.javapostsforlearning.jaxb;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElementWrapper;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
//Below annotation defines root element of XML file
@XmlRootElement
//You can define order in which elements will be created in XML file
//Optional
@XmlType(propOrder = { "countryName", "countryPopulation", "listOfStates"})
public class Country {
private String countryName;
private double countryPopulation;
private ArrayList<state> listOfStates;
public Country() {
}
public String getCountryName() {
return countryName;
}
@XmlElement
public void setCountryName(String countryName) {
this.countryName = countryName;
}
public double getCountryPopulation() {
return countryPopulation;
}
@XmlElement
public void setCountryPopulation(double countryPopulation) {
this.countryPopulation = countryPopulation;
}
public ArrayList<state> getListOfStates() {
return listOfStates;
}
// XmLElementWrapper generates a wrapper element around XML representation
@XmlElementWrapper(name = "stateList")
// XmlElement sets the name of the entities in collection
@XmlElement(name = "state")
public void setListOfStates(ArrayList<state> listOfStates) {
this.listOfStates = listOfStates;
}
}
@XmlType(propOrder = {"list of attributes in order"}):This is used to define order of elements in XML file.This is optional.
@XmlElement:This is used to define element in XML file.It sets name of entity. @XmlElementWrapper(name = "name to be given to that wrapper"):It generates a wrapper element around XML representation.E.g.In above example, it will generate <stateList>
2.State.java
package org.arpit.javapostsforlearning.jaxb;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
//Below statement means that class "Country.java" is the root-element of our example
@XmlRootElement(namespace = "org.arpit.javapostsforlearning.jaxb.Country")
public class State {
private String stateName;
long statePopulation;
public State()
{
}
public State(String stateName, long statePopulation) {
super();
this.stateName = stateName;
this.statePopulation = statePopulation;
}
public String getStateName() {
return stateName;
}
public void setStateName(String stateName) {
this.stateName = stateName;
}
public long getStatePopulation() {
return statePopulation;
}
public void setStatePopulation(long statePopulation) {
this.statePopulation = statePopulation;
}
}
3.JAXBJavaToXml.java
package org.arpit.javapostsforlearning.jaxb;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBException;
import javax.xml.bind.Marshaller;
public class JAXBJavaToXml {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// creating country object
Country countryIndia=new Country();
countryIndia.setCountryName("India");
countryIndia.setCountryPopulation(5000000);
// Creating listOfStates
ArrayList<state> stateList=new ArrayList<state>();
State mpState=new State("Madhya Pradesh",1000000);
stateList.add(mpState);
State maharastraState=new State("Maharastra",2000000);
stateList.add(maharastraState);
countryIndia.setListOfStates(stateList);
try {
// create JAXB context and initializing Marshaller
JAXBContext jaxbContext = JAXBContext.newInstance(Country.class);
Marshaller jaxbMarshaller = jaxbContext.createMarshaller();
// for getting nice formatted output
jaxbMarshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, Boolean.TRUE);
//specify the location and name of xml file to be created
File XMLfile = new File("C:\\arpit\\CountryRecord.xml");
// Writing to XML file
jaxbMarshaller.marshal(countryIndia, XMLfile);
// Writing to console
jaxbMarshaller.marshal(countryIndia, System.out);
} catch (JAXBException e) {
// some exception occured
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
After running above program,you will get following output
Console output:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<country xmlns:ns2="org.arpit.javapostsforlearning.jaxb.Country">
<countryName>India</countryName>
<countryPopulation>5000000.0</countryPopulation>
<stateList>
<state>
<stateName>Madhya Pradesh</stateName>
<statePopulation>1000000</statePopulation>
</state>
<state>
<stateName>Maharastra</stateName>
<statePopulation>2000000</statePopulation>
</state>
</stateList>
</country>
Now we will read above generated XML and retrieve country object from it.
4.JAXBXMLToJava.java
package org.arpit.javapostsforlearning.jaxb;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBException;
import javax.xml.bind.Unmarshaller;
public class JAXBXMLToJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// create JAXB context and initializing Marshaller
JAXBContext jaxbContext = JAXBContext.newInstance(Country.class);
Unmarshaller jaxbUnmarshaller = jaxbContext.createUnmarshaller();
// specify the location and name of xml file to be read
File XMLfile = new File("C:\\arpit\\CountryRecord.xml");
// this will create Java object - country from the XML file
Country countryIndia = (Country) jaxbUnmarshaller.unmarshal(XMLfile);
System.out.println("Country Name: "+countryIndia.getCountryName());
System.out.println("Country Population: "+countryIndia.getCountryPopulation());
ArrayList<state> listOfStates=countryIndia.getListOfStates();
int i=0;
for(State state:listOfStates)
{
i++;
System.out.println("State:"+i+" "+state.getStateName());
}
} catch (JAXBException e) {
// some exception occured
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
After running above program,you will get following output
Console output:
Country Name: India
Country Population: 5000000.0
State:1 Madhya Pradesh
State:2 Maharastra
JAXB advantages:
- It is very simple to use than DOM or SAX parser
- We can marshal XML file to other data targets like inputStream,URL,DOM node.
- We can unmarshal XML file from other data targets.
- We don't need to be aware of XML parsing techniques.
- We don't need to access XML in tree structure always.
JAXB disadvantages:
- JAXB is high layer API so it has less control on parsing than SAX or DOM.
- It has some overhead tasks so it is slower than SAX.
Source code:
Source:Download


No comments:
Post a Comment