This is 2 of 13 parts of tutorial series
i.e., Applying IoC, objects are given their dependencies at creation time by some external entity that coordinates each object in the system. That is, dependencies are injected into objects. So, IoC means an inversion of responsibility with regard to how an object obtains references to collaborating objects.
Normal way:
In next post we will see spring hello world program in spring.
Tutorial Content:
The basic concept of the dependency injection (also known as Inversion of Control pattern) is that you do not create your objects but describe how they should be created. You don't directly connect your components and services together in code but describe which services are needed by which components in a configuration file. A container (in the case of the Spring framework, the IOC container) is then responsible for hooking it all up.
Part-1:Introduction to spring framework
Part-2:Dependency injection(ioc) in spring
Part-3:Spring hello world example in eclipse
Part-4:Dependency injection via setter method in spring
Part-5:Dependency injection via constructor in spring
Part-6:Spring Bean scopes with examples
Part-7:Initializing collections in spring
Part-8:Beans Autowiring in spring
Part-9:Inheritance in Spring
Part-10:Spring ApplicationContext
Part-11:Spring lifetime callbacks
Part-12:BeanPostProcessors in Spring
Part-13:Annotation based Configuration in spring
i.e., Applying IoC, objects are given their dependencies at creation time by some external entity that coordinates each object in the system. That is, dependencies are injected into objects. So, IoC means an inversion of responsibility with regard to how an object obtains references to collaborating objects.
Example:
Lets we have two classes-Car and Engine.Car has a object of Engine.
There are many ways to instantiate a object. A simple and common way is with new operator.
so here Car class contain object of Engine and we have it instantiated using new operator.
 |
Without DI |
With help of Dependency Injection:
Now we outsource instantiation and supply job of instantiating to third party.Car needs object of Engine to operate but it outsources that job to some third party. The designated third party, decides the moment of instantiation and the type to use to create the instance. The dependency between class Car and class Engine is injected by a third party. Whole of this agreement involves some configuration information too. This whole process is called dependency injection.
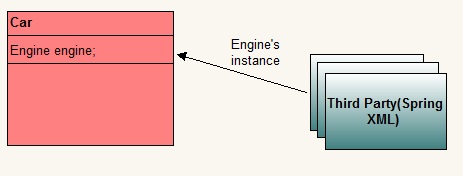 |
With DI |
How this whole dependency injection works,we will see it in further posts.
Benifits of Dependency Injection in Spring:
- Ensures configuration and uses of services are separate.
- Can switch implementations by just changing configuration.
- Enhances Testability as mock dependencies can be injected.
- Dependencies can be easily identified.
- No need to read code to see what dependencies your code talks to.
Types of Dependency Injection:
- Inteface Injection: In interface-based dependency injection, we will have an interface and on implementing it we will get the instance injected.
In next post we will see spring hello world program in spring.

